Published in Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol 15, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1475385
Abstract
Overflow metabolism is a well-known phenomenon that describes the seemingly wasteful and incomplete substrate oxidation by aerobic cells, such as yeasts, bacteria, and mammalian cells, even when conditions allow for total combustion via respiration. This cellular response, triggered by an excess of C-source, has not yet been investigated in archaea.
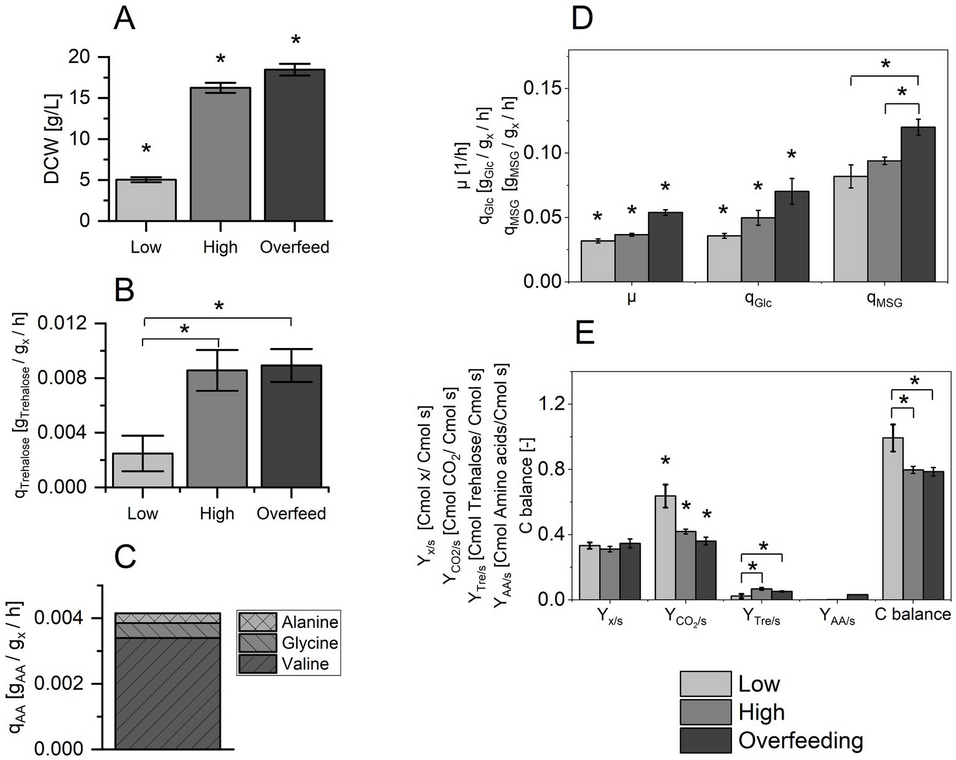
In this study, we conducted chemostat cultivations to compare the metabolic and physiological states of the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius under three conditions, each with gradually increasing nutrient stress. Our results show that S. acidocaldarius has different capacities for the uptake of the two C-sources, monosodium glutamate and glucose.
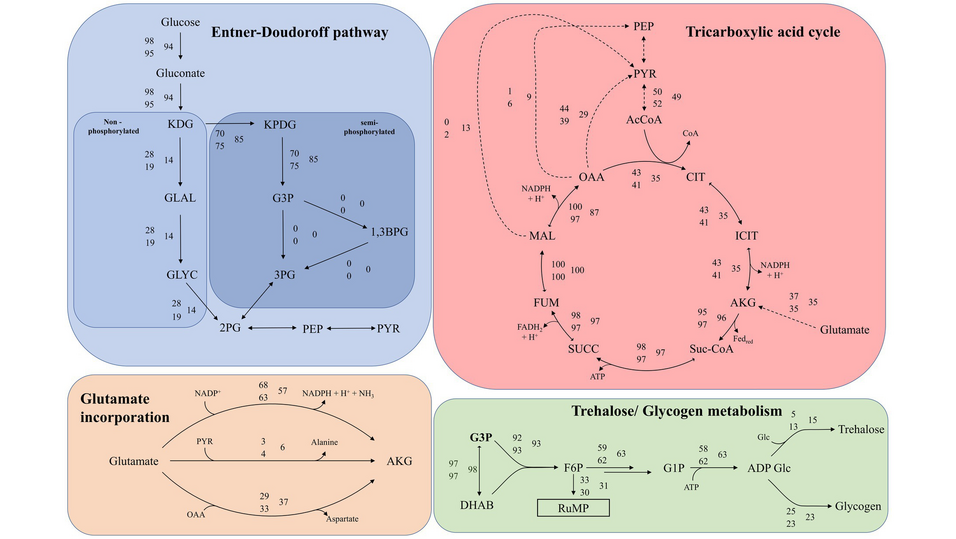
A saturated tricarboxylic acid cycle at elevated nutrient concentrations affects the cell’s ability to deplete its intermediates. This includes deploying additional cataplerotic pathways and the secretion of amino acids, notably valine, glycine, and alanine, while glucose is increasingly metabolized via glycogenesis. We did not observe the secretion of common fermentation products, like organic acids.
Transcriptomic analysis indicated an upregulation of genes involved in fatty acid metabolism, suggesting the intracellular conservation of energy. Adapting respiratory enzymes under nutrient stress indicated high metabolic flexibility and robust regulatory mechanisms in this archaeon. This study enhances our fundamental understanding of the metabolism of S. acidocaldarius.